M.2 SSD Tier List
The sequential read and write speeds, which are usually the most advertised number, are not a proper benchmark of real-world performance or the quality of an SSD. This article categorizes and tiers SSDs based on factors like the type of NAND flash, the controller, the interface and the type of caching used, which will be of better help when comparing SSDs.

This tier list only compares NVMe M.2 drives with a PCIe 4x4 or PCIe 5x4 interface
M.2 drives with a SATA interface are usually worse than Tier C
M.2 NVMe drives with a PCIe 3x4 interface can fall anywhere in Tier B or lower based on the factors used below.
S Tier
- These are Gen5 SSDs with DRAM Cache
- Sequential read and write speeds upwards of 11,000 and 12,000 MB/s respectively.

DRAM Caching is a feature of SSDs where a small amount of super-fast LPDDR4 memory is present to handle smaller files, greatly improving the performance on small files, random read/writes and initial sequential write speeds.
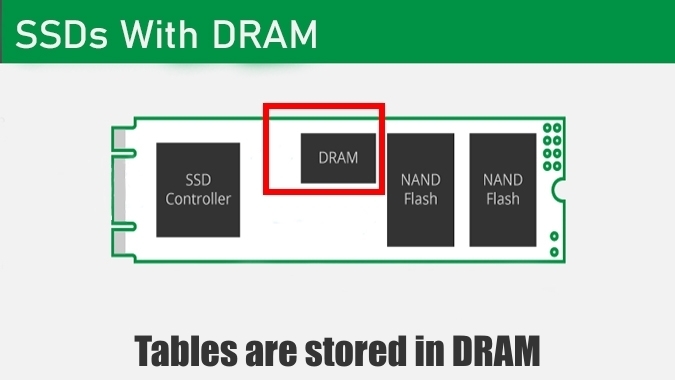
- Steady state write speeds are above 3000 MB/s
MBUZZ Products: Crucial T700, T-Force Z540
Other Products: Corsair MP700
A+ Tier
- These are Gen4 SSDs with DRAM Cache
- A+ Tier SSDs achieve sequential read and write speeds upwards of 6500 and 7000 MB/s respectively.

Most SSDs implement a write cache, which is a fast area of (usually) pseudo-SLC (Single Layer) programmed flash that absorbs incoming data. Sustained write speeds can suffer once the workload spills outside of the cache, DRAM and p-SLC, and into the "native" TLC (Triple Layer) or QLC (Quad Layer) flash when writing huge amounts of data.
- Steady state write speeds for A+ Tier are above 1200 MB/s
MBUZZ Products: Crucial T500, T-Force A440, Lexar NM800
Other Products: Samsung 990 Pro, WD SN850X
A Tier
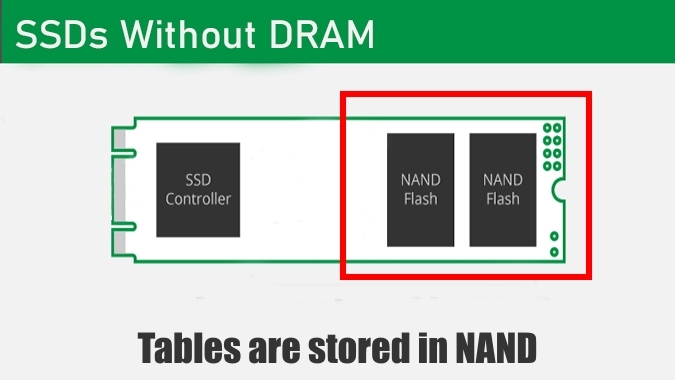
- A Tier consists of Gen4 SSDs with pseudo-SLC + HMB Cache
- Achieve sequential read and write speeds upwards of 6500 and 7000 MB/s respectively.
- These SSDs have excellent controllers which helps the random performance come close to the A+ Tier SSDs while consuming less power.

HMB Caching is a feature of newer NVMe SSDs to use the memory of the host computer for caching
- Steady state write speeds for A Tier are above 1000 MB/s
MBUZZ Products: Lexar NM790, Team MP44
Other Products: Samsung 980/980 Pro*, WD SN850*
 SSDs like Crucial P5 Plus, Samsung 980 Pro, WD SN850 have sub 6500/7000 MB/s peak sequential speeds but with DRAM Caching.
SSDs like Crucial P5 Plus, Samsung 980 Pro, WD SN850 have sub 6500/7000 MB/s peak sequential speeds but with DRAM Caching.Such SSDs, marked with *, are also considered part of Tier A
B Tier
- These are Gen4 DRAM-less SSDs with TLC Nand
- B Tier SSDs have sequential read and write speeds upwards of 3500 and 4000 MB/s respectively.

SSDs use non-volatile flash memory called NAND flash to store data. They can be classified based on the amount of data stored per cell of NAND flash as SLC, MLC, TLC or QLC as shown below:

As Data stored per cell increases, endurance, price and performance decreases. B-Tier and higher SSDs use TLC or better. QLC is slower, cheaper, and has less endurance. Even though caching helps, QLC SSDs will be slower and will have very poor steady state write speeds in M.2 SSDs
- Steady state write speeds for B Tier are above 1000 MB/s
MBUZZ Products: Team MP44L, Lexar NM710
Other Products: WD SN770
C+ Tier
- These are Gen4 SSDs with QLC NAND and DRAM Cache
- Tier C+ SSDs have peak read and write speeds of at least 4000 and 3000 MB/s respectively.
- Steady state write speeds for C+ Tier are around 300 MB/s
MBUZZ Products: T-Force Z44Q
Other Products: Sabrent Rocket Q4, Corsair MP600 Core
C Tier
- These are Gen4 SSDs with QLC NAND and pseudo-SLC + HMB Cache
- Tier C+ SSDs have sequential read and write speeds around 4000 and 3000 MB/s respectively.
- Steady state write speeds for C Tier are around 300 MB/s
MBUZZ Products: Crucial P3 Plus
Other Products: Kingston NV2, Solidigm P41 Plus
References:
Related Articles
What Do You Need for a Custom Build PC?
What Do You Need for a Custom Build PC? To create a custom-built PC, you'll need several components. Regardless of your experience level, using a tool like PCPartPicker is recommended to ensure compatibility and manage your budget effectively. Here's ...NVIDIA L20 vs. L40: A Deep Dive into Performance and Capabilities for AI and Professional Workloads
When it comes to choosing the right GPU for AI and professional workloads, NVIDIA's L20 and L40, based on the Ada Lovelace architecture, are both stellar options. As someone who is spent considerable time exploring these technologies, I have found ...AMD Ryzen AM4 Motherboard CPU Compatibility
For the AM4 Platform, AMD has been very generous when it comes to motherboard compatibility. A CPU launched in 2022, like the Ryzen 7 5800X3D, will work with an almost 6-year-old motherboard, like the ASRock X370 Pro, which was launched in early ...Stage of Project Planning in project management
Project planning is a crucial stage in project management that involves defining the project scope, objectives, and the detailed plan for how the project will be executed. This stage helps ensure that the project is well-organized, on track, and that ...Roles & Responsibilities of A Project Manager
A project manager plays a crucial role in planning, executing, and closing a project. Their responsibilities can vary depending on the organization and the specific project, but here are some common roles and responsibilities of a project manager: ...