iSCSI and its Usecases in Briefcam
iSCSI Overview
iSCSI (Internet Small Computer Systems Interface) is a
network protocol that allows for the transport of block-level storage data over
IP networks. Essentially, iSCSI enables servers (initiators) to connect to
storage devices (targets) across local area networks (LANs), wide area networks
(WANs), or even the internet. This provides a way to centralize storage in data
centers or extend the storage available to servers without the need for
direct-attached storage.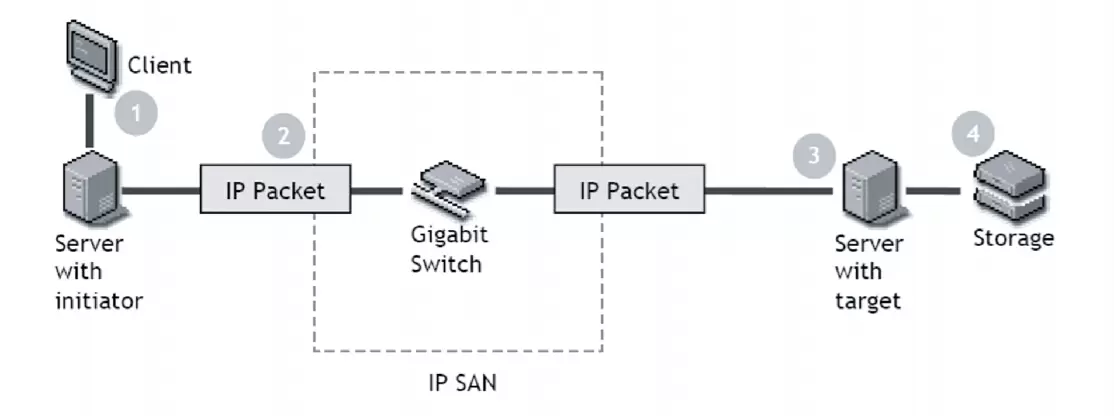
- Initiator: The client that connects to the storage
(typically a server).
- Target: The storage device or storage server that is made
available to the initiator.
iSCSI allows data centers to
consolidate storage into centralized pools, simplifying management and
increasing utilization efficiency. Storage administrators can manage and
allocate storage without being tied to the physical proximity of the servers.
With iSCSI, storage can be
replicated to offsite locations over IP networks, providing a reliable way to
implement disaster recovery solutions. Backups can be performed over the
network to remote storage targets, offering redundancy in case of failures.
In virtualized environments (e.g.,
using VMware or Hyper-V), iSCSI allows virtual machines to access centralized
storage, facilitating easier management of storage resources and supporting
live migrations like VMware’s vMotion.
iSCSI enables the creation of
SANs without the need for expensive Fibre Channel infrastructure. This reduces
costs while still providing many of the benefits of SANs, such as improved
storage scalability, availability, and performance.
iSCSI facilitates accessing data across
different geographic locations, which is especially useful for organizations
that have distributed data centers or branch offices.

BriefCam generates large amounts of video
data, and iSCSI can be used to store this data efficiently in centralized
storage repositories. This allows for scalable, high-performance storage that
is necessary for managing continuous video streams.
BriefCam software might need
storage that scales as the video footage accumulates over time. iSCSI enables
this scalability, allowing storage administrators to dynamically expand storage
capacity as needed.
Surveillance systems
require high uptime and reliable storage. iSCSI can be used in conjunction with
storage redundancy technologies (like RAID) to ensure that video data is
available at all times, even in case of hardware failure.
BriefCam’s analytics and video
processing can take advantage of iSCSI’s centralized storage model to quickly
retrieve and process video data. This improves the efficiency of generating
insights and alerts based on video feeds.
Additional Benefits
iSCSI is a flexible, cost-effective way to implement storage
solutions across IP networks. It is particularly useful in data centers for
storage centralization, disaster recovery, and virtualization support. For
software like BriefCam, which handles significant volumes of video data, iSCSI
allows for scalable, reliable storage that is essential for effective video
analysis and management.Related Articles
How to enable SAN Connectivity and RAID Controller using HBA Card?
HBA Card is used for enabling communication between servers and storage devices SAN (Storage Area Network A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a specialized, high-speed network that provides block-level network access to storage RAID Controller RAID ...Troubleshooting storage drive not detected
A storage drive not being detected can be due to a variety of factors, and the solution depends on the underlying cause. Here are some of the major parameters or reasons why a storage drive may not be detected and the corresponding solutions: Cable ...Lexar JumpDrive Fingerprint F35 Flash Drive Manual
Contents Before You Start ................................................................................. 1 For Users ............................................................................................................... 1 Specifications ...Container on Proxmox
Upload Container Template on Proxmox Storage Go to the server Select storage in which you want upload template Go to "CT Templates" tab Click on "Templates" button Search for Templates You can search any kind of Linux flavour Select Package and click ...Set up RAID 0 using mdadm
Steps to configure RAID 0 in Centos7. Code lsblk yum install -y mdadm mdadm --create --verbose /dev/md0 --level=0 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdb /dev/sdc mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0 mkdir /mnt/raid0-drive mount /dev/md0 /mnt/raid0-drive df -h Code Summary LSBLK: - ...